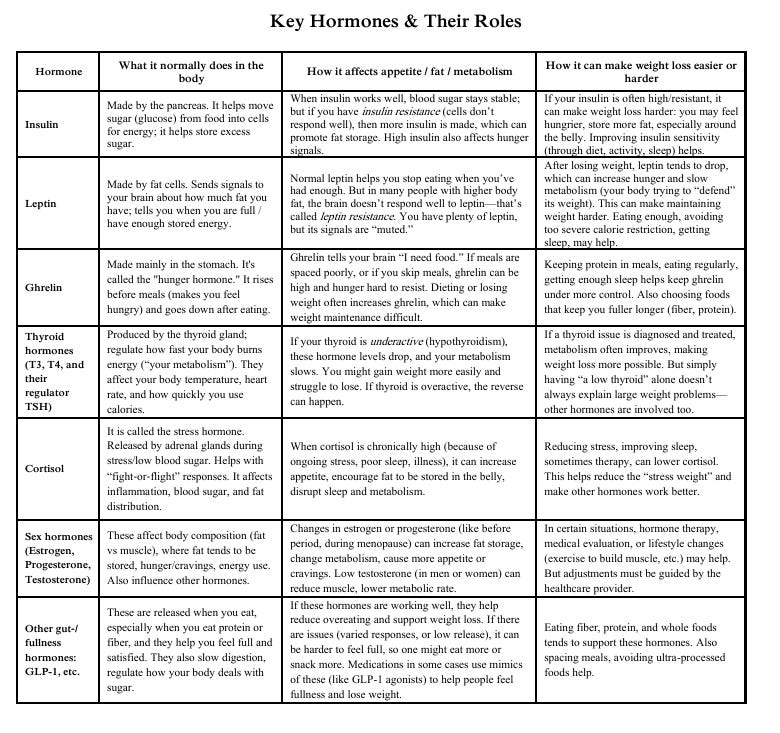
Hormones are chemical messengers in your body. They tell organs what to do—for example, when to eat, when to burn energy, when to store fat. Sometimes weight loss or trouble losing weight is not just about willpower or calories— It can also involve how your hormones work. Understanding them can help you plan better, talk with your doctor, and make changes that support your body. Here are key hormones, what they do, how they’re involved in weight loss (or lack of), and what you might do to help them.
How Hormones Can Make Losing Weight Hard Here are some examples of hormonal situations that can make weight loss more difficult: Leptin resistance: You have fat stores, leptin is high, but your brain isn’t getting the “you’re full / stop eating” message well. Insulin resistance: Same idea—your body makes more insulin, sugar doesn’t enter cells as well, more gets stored as fat; blood sugar swings, hunger, fatigue. High ghrelin + low leptin after dieting: If you restrict calories a lot, your ghrelin often goes up (makes you hungrier) and leptin goes down (so less signal you’re full). That makes sticking with weight loss harder. Chronic stress / high cortisol: Stress makes you more likely to eat high-sugar or high-fat comfort foods, and cortisol also directs more fat to the belly. Poor sleep: Sleep deprivation messes with insulin, leptin, ghrelin—all of them. You can get hungrier, eat more, and have worse glucose handling. Underlying medical conditions: Hypothyroidism, PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome), low sex hormones, etc., can shift hormone balance so that metabolism is slower, you store fat more easily, or hunger signals are stronger/weaker in unhelpful ways. What Can You Do to Help Hormones Work in Your Favor These are tried, generally safe strategies to improve hormone balance and support weight loss. Different things work better for different people—talk with your healthcare provider especially if you suspect there’s a hormonal disorder.
What Your Body Is Trying to Do It helps to think of your body as having set points or “default weight ranges” it tends to protect. When you lose weight: • Your body may slow metabolism (burn fewer calorie) • Hunger hormones may increase, fullness hormones decrease • Your body may burn fewer calories for the same activity These are protective mechanisms—they helped humans survive when food was scarce. But today, they make weight loss and especially keeping weight off more challenging. Bottom Line • Hormones are powerful players in hunger, fullness, energy use, and fat storage. • They can make losing weight harder—but many times, lifestyle changes can help them work better. • Sustainable weight loss generally comes from steady, balanced changes (diet, activity, sleep, stress).